E for Fat
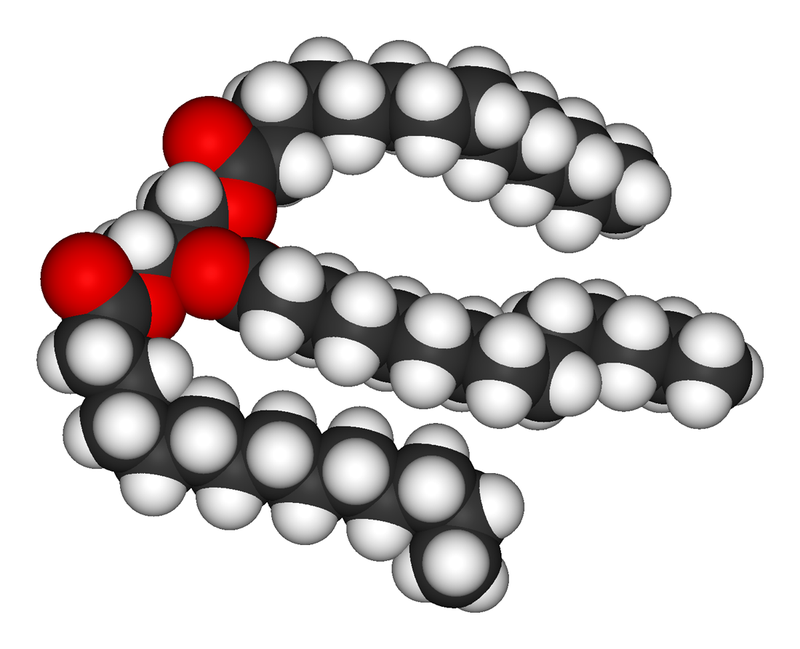
Each fat is a derivative of fatty acids and glycerol. Three chains of fatty acid are bonded to each of the three -OH groups of the glycerol by the reaction of the carboxyl end of the fatty acid (-COOH) with the alcohol. HOH (water) is eliminated and the carbons are linked by an -O- bond through dehydration synthesis. This process is called esterification and fats are therefore esters. As a simple visual illustration, if the kinks and angles of these chains were straightened out, the molecule would have the shape of a capital letter E. The fatty acids would each be a horizontal line and the glycerol “backbone” would be the vertical line that joins the horizontal lines.